A Novel Pilot Study Using Spatial Frequency Domain Imaging to Assess Oxygenation of Perforator Flaps During Reconstructive Breast Surgery
Nguyen JT, Lin SJ, Tobias AM, Gioux S, Mazhar A, Cuccia DK, Ashitate Y, Stockdale A, Oketoun R, Durr NJ, Moffitt LA, Durkin AJ, Tromberg BJ, Frangioni JV, Lee BT.
Annals of Plastic Surgery 71:3 2013.
DOI: 10.1097/SAP.0b013e31828b02fb
Introduction
Although various methods exist for monitoring flaps during reconstructive surgery, surgeons primarily rely on assessment of clinical judgment. Early detection of vascular complications improves rate of flap salvage. Spatial frequency domain imaging (SFDI) is a promising new technology that provides oxygenation images over a large field of view. The goal of this clinical pilot study is to use SFDI in perforator flap breast reconstruction.
Methods
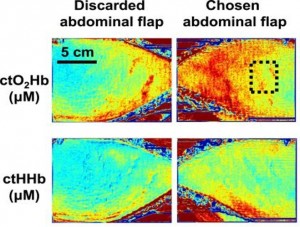
Three women undergoing unilateral breast reconstruction after mastectomy were enrolled for our study. The SFDI system was deployed in the operating room, and images acquired over the course of the operation. Time points included images of each hemiabdominal skin flap before elevation, the selected flap after perforator dissection, and after microsurgical transfer.
Results
Spatial frequency domain imaging was able to measure tissue oxy-hemoglobin concentration (ctO2Hb), tissue deoxyhemoglobin concentration, and tissue oxygen saturation (stO2). Images were created for each metric to monitor flap status and the results quantified throughout the various time points of the procedure. For 2 of 3 patients, the chosen flap had a higher ctO2Hb and stO2. For 1 patient, the chosen flap had lower ctO2Hb and stO2. There were no perfusion deficits observed based on SFDI and clinical follow-up.
Conclusions
The results of our initial human pilot study suggest that SFDI has the potential to provide intraoperative oxygenation images in real-time during surgery. With the use of this technology, surgeons can obtain tissue oxygenation and hemoglobin concentration maps to assist in intraoperative planning; this can potentially prevent complications and improve clinical outcome.
Keywords: perforator flap, breast reconstruction, microsurgery, perfusion mapping, near-infrared imaging, spatial frequency domain imaging